Hacking consumer AI for Library Discovery
13 Jul 2017Note: this post is still a work in progress
For the VALA Tech Camp 2017 I’ve been asked to do workshop on ‘Hacking consumer AI for Library Discovery’. In this blog post and the workshop I’ll run through how to utilise consumer AI (in this example Amazon Alexa) to work with a library discovery service (Trove)

Note: Trove is the National Library of Australia’s discovery service and more. You can read more about Trove at http://trove.nla.gov.au/general/about
End Result: Be able to talk to Trove using Alexa.
Objective: Create an Alexa ‘skill’ that can query the Trove API
Services we are going to use:
- Trove API
- AWS Lambda
- AWS Alexa/Echo
- Echosim.com
Requirements:
- Trove API key (recommended)
- Create a Trove account at https://trove.nla.gov.au/signup
- Then apply for a Trove API key on the ‘For developers‘ page
- http://trove.nla.gov.au/userProfile#developer
- Select non-commercial API purposes
- And the purpose entre ‘Development of Amazon Echo to Trove API app’
- An API key should then be immediately available
- Amazon AWS account (required)
- A free account can be created at https://aws.amazon.com/
- Amazon Developers portal access (required)
- Create/login to https://developer.amazon.com using the same account as the AWS account
- GitHub account is not required but recommended
Alexa skills
First up we’ll details what an Alexa skill is.
An Alexa skill is a services that adds extra functioanlity to your Amazon Alexa/Echo device. In this workshop we’ll be creating a skill called Trove Australia. The main techincal parts of a skill are:
- Invoication Name
- Intents
- Utterances
Each Alexa skill is comprised of an Invocation Name which you can think of as your app name, a set of Intents and the phrases that map to each intent, and the software that can detect the intent and return an appropriate result. These Intents are are executed by Alexa when a user says a specific Utterance. We’ll dive deeper into each of these later
The skill we’re going to build is going to be an basic enough program that queries Trove for random book.
Skill Steps
Building your first skill will comprise of four steps. First we’re going to copy the ‘Trove’ code into Amazon Lambda, which will be responsible for running the code. Next we’re going to set up our skill in the Amazon Alexa Skills Developer Portal, and link our lambda account to that skill. Then we’re going to test using the Amazon service simulator and on an Alexa-enabled device. Lastly, we’ll walk through the steps of customizing your skill to your needs.
Step 1: AWS Lambda

- Open the AWS Lambda console
- Login or create an account with the same Amazon account that your Alexa device is linked to.
Next we’ll create a Lambda function that weill talk to the Trove API
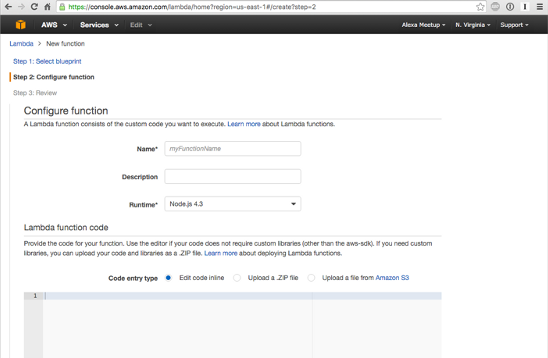
In the AWS Lambda console click Create a Lambda function, then in the Slect blueporint screen - select Python 3.6 from the Runtime dropdown and click the Blank function. In the ‘Configure triggers’ screen click on the dotted grey box and select Alexa Skills Kit. This setups the basic lambda function ready for Alexa.
In Configure function
Enter the name and description of your Lambda function. It’s not very important what the name is but it needs to be unique, you can just use “Trove”. In the top right it should say “N. Virginia”. If that’s not the case please select “US-East (N. Virginia)” from the dropdown.
Why North Virginia? As of the time of this writing, the Alexa Skills Kit is only hosted in East US (N. Virginia.)
Remember to set Python 3.5 as the Runtime
Source code
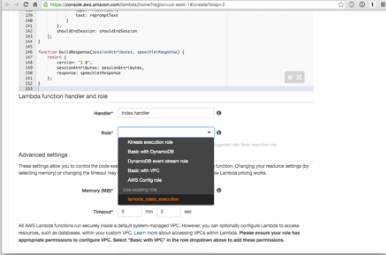
In the code section you get the option to either enter the code inline or upload a zip file. As the code we are using requires a few extra Python modules we’ll chouse the zip option.
Download the zip I’ve already prepared of the full source code for the Trove skill and upload it in to the Function Package section of the page
For those wondering what this code we are about to upload actual does, below is the main sample. This is a very simple Alexa skill that queries (based on a random word) the Trove API for a book. Very simple but a great intro to shows what Alexa can do.
_https://github.com/justinkelly/alexa/blob/master/src/lambda_function.py
def get_trove_query(intent, session):
card_title = intent['name']
session_attributes = {}
should_end_session = True
word_site = "https://raw.githubusercontent.com/paritytech/wordlist/master/res/wordlist.txt"
response = requests.get(word_site)
WORDS = response.content.splitlines()
searchquery = random.choice(WORDS)
trove_api_key = os.environ['TROVE_API_KEY']
troveURL = 'http://api.trove.nla.gov.au/'
r = requests.get(troveURL + 'result/', params = {
'key': trove_api_key,
'zone': 'book',
'encoding': 'json',
'q': searchquery
} )
#r.encoding = 'ISO-8859-1'
results=r.json()
trove_book_title = results['response']['zone'][0]['records']['work'][0]['title']
trove_book_title = trove_book_title.replace(":", " ")
trove_book_title = trove_book_title.replace("/", " by the author ")
final_data = "For the random word " + searchquery + " Trove has found the book " + trove_book_title
Back in Lambda, you’re going to scroll down a bit and we are going to enter our Trove API key as an environment variable. This allows the Python script to access the API without us having to store it directly in the file.
In the key section enter TROVE_API_KEY and in the field to the right of it paste in your Trove API key
The next step not to miss that is very important is the Handler section. Enter lambda_function.lambda_handler in this field. This field tells Lambda the file_name and function to run.
Scroll down a bit further to the “Lambda function handler and role” section. You’re going to want to set the role to “lambda_basic_execution”. It’s important to note that if this is your first time using Lambda, you’ll have to create the “lambda_basic_execution” role. You can do that by selecting the first option “* Basic Execution” and clicking the blue button on the next page. After you take that step, you should be able to select “lambda_basic_execution”.
Next expand the ‘Advanced settings’ section and increase the timeout from 3 seconds to 10 (or more). This is if the Trove API is slow to respond the Lambda function wont auto timeout.
Click Next to review the function. If the Triggers section is empty make sure to add the Alexa Skills Kit and then click Create function
Please note if you’ve never signed up for the Amazon Developer Portal, you’ll have to do that first before the “Alexa Skills Kit” will appear. Please also make sure you use the same Amazon account as the one you’re using for AWS and your Echo.
Step 1 Done
Your first Lambda function is now complete :)
Keep the Amazon Lambda tab open though, we’ll need to come back to it!
Step 2: AWS Developer skills
Open the Amazon Developer Alexa Skills portal and login with the same Amazon account that your Alexa device is linked with.
Navigate to Add New Skill and click the yellow “Get Started >” button under “Alexa Skills Kit”, then the yellow “Add a New Skill” button on the next page.
The name of your Amazon Alexa skill must be unique for your account, and the invocation name is what you’ll use to activate the skill. “Alexa, tell
Interaction Model
Here is where we’re going to tell the skill which intents we support, and what type of words will trigger each intent. Get ready for some copy and pasting.
Amazon have a new tool available that simplfies this previously complex section - You should be a Interaction Model Buidler BETA
Once in the new BETA tool go to the code editor section and copy/paste in the below code - this code tell ALexa what are intents are goign to be and what utterances are defined for each intent
{
"intents": [
{
"name": "AMAZON.CancelIntent",
"samples": []
},
{
"name": "AMAZON.HelpIntent",
"samples": []
},
{
"name": "AMAZON.PauseIntent",
"samples": []
},
{
"name": "AMAZON.ResumeIntent",
"samples": []
},
{
"name": "AMAZON.StopIntent",
"samples": []
},
{
"name": "queryTrove",
"samples": [
"search",
"random search",
"search random book",
"search book",
"random"
],
"slots": []
}
]
}
Once entered click the Save Model and then Build Model buttons in the top menu and proceded to the next section
Configuration
Change the radio button from HTTPS to Lambda ARN and select the No radio button under Account Linking. Now we’ll have to go and grab the Lambda Amazon Resource Name (ARN) from our Lambda tab.
Copy ARN
The ARN is on the top right of the Lambda function page.
Paste ARN
Paste the ARN into the text field, and press Next.
Step 3 Testing
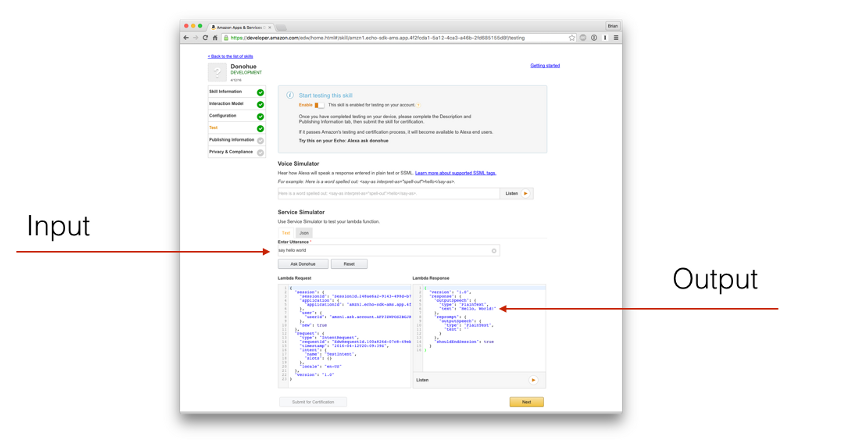
After you click Next on the Configuration tab, you should be on the Test tab. Under the Service Simulator portion you’ll be able to enter a sample utterance to trigger your skill. For the Trove example you should type search random book, and on the right you should see the output from the Lambda function you created: Hello, World!
Adding accounts for testing
One thing that cause be issues when I first created a skill was that the skill wasn’t immediately available for my own account to actual test. The solution of this is to add your amazon account to the list of beta testers for this skill.
Click on the Skills Beta Testing seciton and add in the amazon accoutns you want this new skill availble for testing
In the beta testign section there will be an invitation link for each user. For your own user click on the link and then ‘Enable’ this new skill on your Alexa account.
Testing on a device
If you got the correct output using the Service Simulator, try it on the Amazon Echo. We were using Trove as the invocation name in this presentation, but you should use the invocation name you set previously.
Alexa, ask Trove for a random book
If you don’t have a device you can use the Echosim website to test a virtual Echo. Just login with your Amazon account used earlier and follow the prompts.
Done
Congrats, you just created your first Alexa skill! 👏👏

Links and credits
- Most of the content of this guide is sourced from https://www.pluralsight.com/guides/node-js/amazon-alexa-skill-tutoria by Brian Donohue
- Source code for our Trove skill is on my GitHub account https://github.com/justinkelly/alexa/
